Farm Management Recommendations and Requirements
Farm Management Recommendations and Requirements
Groundwater Nitrate
Nitrate can present a health risk, when present in drinking water in high concentrations. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) set a drinking water quality standard of 10 mg/l of nitrate-nitrogen or 45 mg/l of nitrate, based on the causation of methemoglobinemia in infants and the elderly, but studies have also shown a potential link between high nitrate concentrations and cancer, caused by the formation of nitrosamine compounds in the stomach.
High nitrate concentrations in the groundwater may occur naturally, but usually they result from human influence. Nitrate is highly soluble and water entering the soil from precipitation or irrigation will carry nitrate not used by plants down to the groundwater. Nitrate mainly enters the groundwater from non-point sources (sources that contribute nitrate over a broad area), such as agriculture fertilizers, but it may also enter from point sources (sources that introduce nitrate at a single location), such as feedlots, septic systems, chemical spills, leaking chemical storage facilities, and improperly abandoned wells.
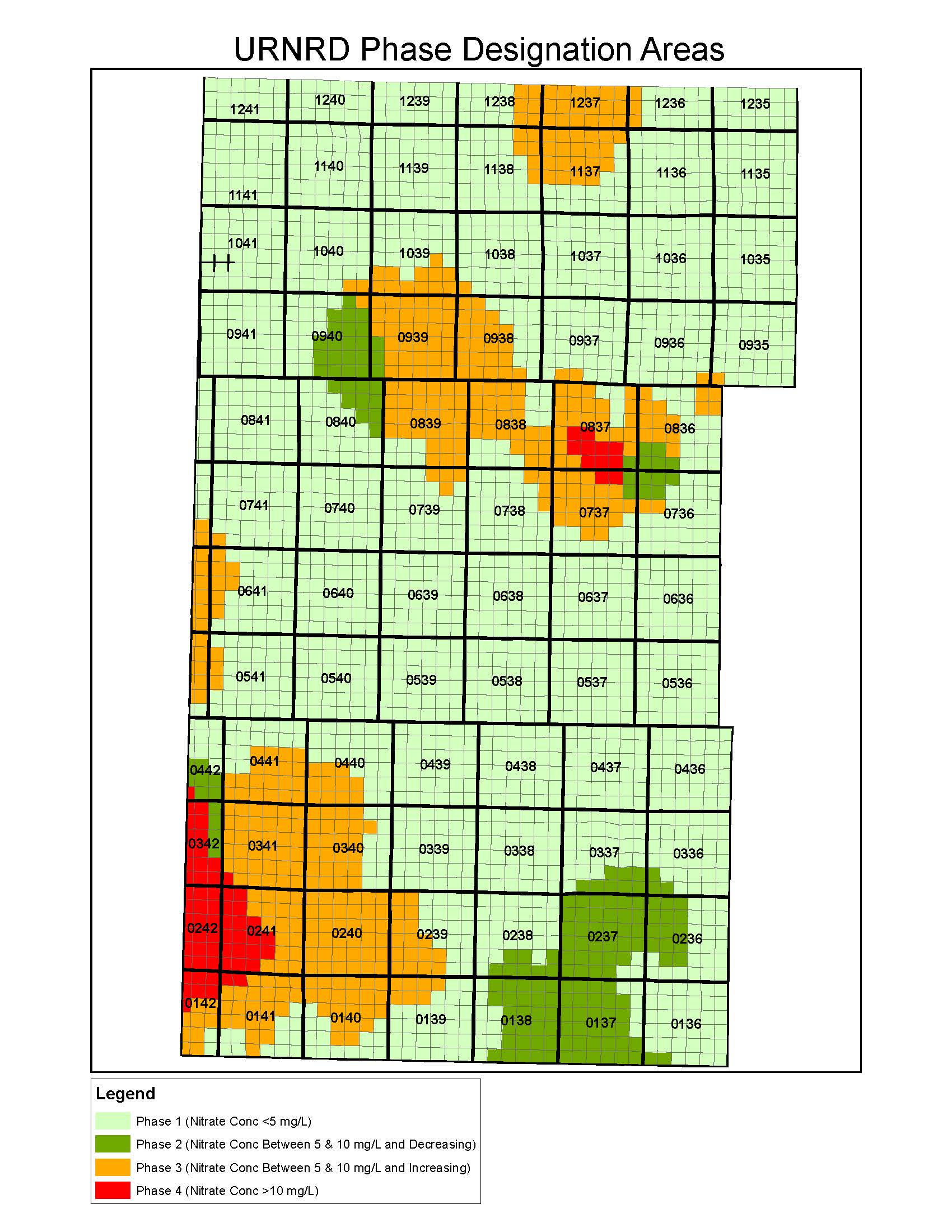
Phase Designation Areas
The District collects and analyzes water samples from irrigation wells throughout the District every summer to estimate the nitrate-nitrogen concentration in our groundwater. While most of the District has relatively good water quality, some areas have higher nitrate concentrations, and in those areas the URNRD requires landowners and operators to follow farm management practices that will maintain or reduce nitrate concentrations in the groundwater. The District is divided into four Phase Designation Areas based on the nitrate-nitrogen concentration and whether the concentration is increasing or decreasing. Each phase designation has different fertilizer and farm management recommendations and/or requirements.
A Phase I Designation Area is an area within the District in which the nitrate-nitrogen concentration is less than 5.0 mg/l. A Phase II Designation Area is an area within the District in which the nitrate-nitrogen concentration is between 5.0 mg/l and 10.0 mg/l, is decreasing over the past 5 years, and contains more than 50% of six adjacent sections. A Phase III Designation Area is where the nitrate-nitrogen concentration in the groundwater is between 5 mg/l and 10 mg/l, is increasing over the past 5 years, and includes more than 50% of six adjacent sections. A Phase IV Designation Area is where the nitrate-nitrogen concentration in the groundwater is greater than 10 mg/l and comprises more than 50% of six adjacent sections. A map of the Phase Designation boundaries is provided below.
The purpose of the phase designation is to identify and monitor the nitrate-nitrogen concentration in the District’s groundwater caused by non-point sources, such as farm practices, and improve aquifer water quality throughout the District.
Phase I Designation Area farm management recommendations include:
- The District recommends that applicators/operators enroll in and review the University of Nebraska-Lincoln (UNL) Extension on-line training program - Irrigation and Nitrogen Management User Education/Certification Program, although the District does not require or offer certification in this program.
- The District recommends that applicators/operators perform soil testing, analyze groundwater quality, and apply nitrogen fertilizer based on the UNL-recommended rates.
- The District recommends that operators use nitrogen inhibitors, slow-release coated fertilizer, or split applications and do not apply fertilizer in fall or winter on row crops.
Phase II Designation Area farm management requirements include:
- All Phase I recommendations apply.
- Prior to November 1 (for the subsequent growing season), applicators/operators may not apply commercial nitrogen fertilizer or liquid manure for row crops.
- After November 1, applicators/operators must use split applications (i.e. pre-plant/pre-emergent and sidedress (post-emergent)) for applications greater than 100 pounds of actual nitrogen/acre or use a nitrification inhibitor or slow-release coated fertilizer. The operator must furnish dealer certification and documentation that the inhibitor or slow-release coated fertilizer was used at the recommended rate, if requested.
Phase III Designation Area farm management requirements include:
- All Phase II Designation Area recommendations and requirements apply.
- Owner/operator must submit an annual online report to the District which includes the crops grown and the fertilizer and water use from the previous year and a procedure that recommends the proper fertilizer rate for the type of crop to be grown and its expected yield for the upcoming growing season.
- Prior to November 1, applicators/operators may not apply commercial nitrogen fertilizer or liquid manure for row crops.
- After November 1 and prior to March 1, applicators/operators may not apply commercial nitrogen fertilizer or liquid manure, except application rates of less than 20 pounds/acre of actual nitrogen on fall or spring seeded crops will be allowed.
- After March 1, applicators/operators must use split applications (i.e. pre-plant/pre-emergent and sidedress (post-emergent)) for applications greater than 100 pounds of actual nitrogen/acre or use a nitrification inhibitor or slow-release coated fertilizer. The operator must furnish dealer certification and documentation that the inhibitor or slow-release coated fertilizer was used at the recommended rate and attached to the online report form.
- Applicators/operators must attend a nitrate and irrigation management education program provided by the URNRD.
- Applicators/operators shall not apply nitrogen fertilizer at rates that exceed crop need based on UNL-recommended fertilizer rates for corn, popcorn, sorghum, potatoes, soybeans, alfalfa, sunflowers, sugar beets, and dry beans. Wheat recommended fertilizer rates are based on recommendations by Colorado State University.
- Applicators/operators must take annual soil samples from fields in which nitrogen fertilizer or manure will be applied. Surface (0 inches to 8 inches) and sub-surface (8 inches to 24 inches) samples must be taken for residual nitrate/nitrogen on each field or 80-acre tract, whichever is smaller, and analyzed by a laboratory participating in the University of Nebraska Soil Testing Program. The results of the analysis shall be attached to the online report form.
- Applicators/operators must conduct irrigation scheduling.
- If manure or sludge is applied to the field, applicators/operators must use a credit for the nitrogen in the manure or sludge in the calculation for the nitrogen fertilizer recommendation. A laboratory analysis must be conducted for each source of manure or sludge and attached to the online report form.
- If the previous year’s crop was a legume (e.g. beans, alfalfa, etc.), applicators/operators must use a credit in the nitrogen fertilizer recommendation.
Phase IV Designation Area farm management requirements include:
- All Phase III Designation Area recommendations and requirements apply.
- Owner/operator must submit an annual online report to the District which includes the crops grown and the fertilizer and water use from the previous year and a procedure that recommends the proper fertilizer rate for the type of crop to be grown and its expected yield for the upcoming growing season.
- Prior to March 1, applicators/operators may not apply commercial nitrogen fertilizer or liquid manure for row crops.
- After March 1, applicators/operators must use split applications (i.e. pre-plant/pre-emergent and sidedress (post-emergent)) for applications greater than 100 pounds of actual nitrogen/acre or use a nitrification inhibitor or slow-release coated fertilizer. The operator must furnish dealer certification and documentation that the inhibitor or slow-release coated fertilizer was used at the recommended rate and attach it to the online report form.
- Applicators/operators must attend a nitrate and irrigation management education program provided by the URNRD.
- Applicators/operators shall not apply nitrogen fertilizer at rates that exceed crop need based on UNL-recommended fertilizer rates for corn, popcorn, sorghum, potatoes, soybeans, alfalfa, sunflowers, sugar beets, and dry beans. Wheat recommended fertilizer rates are based on recommendations by Colorado State University.
- Applicators/operators must take annual soil samples from fields in which nitrogen fertilizer or manure will be applied. Surface (0 inches to 8 inches) and sub-surface (8 inches to 24 inches) samples must be taken for residual nitrate/nitrogen on each field or 80-acre tract, whichever is smaller, analyzed by a laboratory participating in the University of Nebraska Soil Testing Program. The results of the analysis shall be attached to the online report form.
- Applicators/operators must conduct irrigation scheduling.
- If manure or sludge is applied to the field, applicators/operators must use a credit for the nitrogen in the manure or sludge used in the calculation for the nitrogen fertilizer recommendation. A laboratory analysis must be conducted for each source of manure or sludge and attached to the online report form.
- If the previous year’s crop was a legume (e.g. beans, alfalfa, etc.), applicators/operators must use a credit in the nitrogen fertilizer recommendation.
Nitrate Management Reports
If an owner’s or operator’s field is in a Phase III or IV Designation Area, they must complete an annual online Nitrate Management Report. Access to the report will be made available in the future via a website link. We will notify the public of the link when the becomes available online. The first section of the report requests that the operator provide farm management information for the previous year, and the second section of the report guides the operator through the process of estimating the fertilizer rate for the intended type of crop to be grown. It accounts for nitrate-nitrogen available to the crops from the soil, irrigation water, manure, if applied, and legumes, if grown previously.
A nitrate and irrigation management education program provided by the URNRD will show the owner and operator how to complete the report. Additional information and guidance will be provided by calling or emailing the URNRD office.
More information on the URNRD water testing program, nitrate contamination and its health effects, frequently asked questions (FAQs), and nitrate treatment options are provided on the URNRD’s website at www.urnrd.org > Program & Regulations > Water Testing. (Direct link is https://www.urnrd.org/programs-regulations/water-testing.)